Menu
Hemosiderin staining, also known as hemosiderosis, is a medical condition characterized by the accumulation of hemosiderin, an iron-storage complex, in the body. While often benign, hemosiderin staining can sometimes indicate underlying health issues that require attention. This article explores the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for hemosiderin staining to provide a comprehensive understanding of this condition. In simple terms, hemosiderin staining is a brownish discoloration that occurs when the body removes (disposes of) red blood cells.
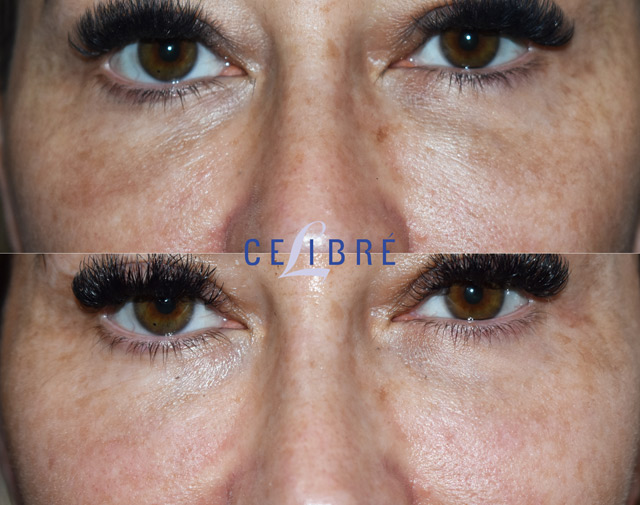
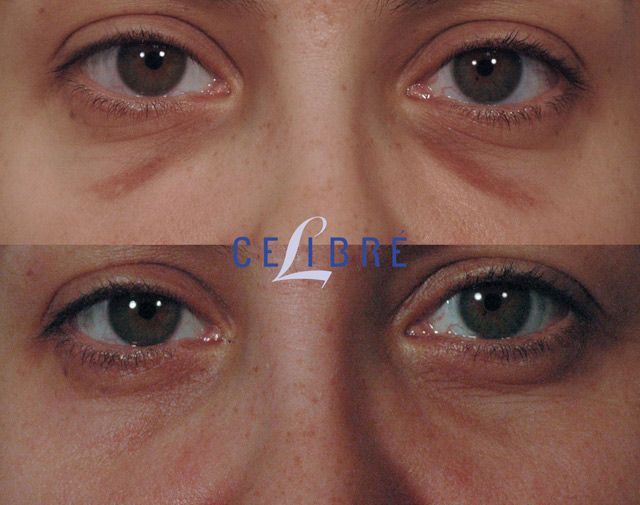


Hemosiderin staining occurs when there is an excess accumulation of hemosiderin in the body. This accumulation can be caused by numerous factors, including:
Venous Insufficiency: One of the primary causes of hemosiderin staining is chronic venous insufficiency (CVI), a condition where the veins in the legs fail to efficiently return blood to the heart. This leads to blood pooling in the lower extremities, causing inflammation, leakage, and eventual breakdown of red blood cells, releasing hemosiderin into the surrounding tissues.
Trauma: Injuries such as very bad bruises, hematomas (large bleed under the skin), or cosmetic procedures including under eye injections, blepharoplasty (eye surgery) and rhinoplasty (nose surgery), can result in the release of red blood cells and subsequent accumulation of hemosiderin in the affected area.
Chronic Inflammation: Conditions associated with chronic inflammation, such as dermatitis or eczema, can lead to hemosiderin staining due to the increased breakdown of red blood cells and leakage of hemosiderin into the surrounding tissues.
Iron Overload Disorders: Certain medical conditions, such as hemochromatosis, can cause an overload of iron in the body, leading to the deposition of hemosiderin in various organs and tissues.
The symptoms of hemosiderin staining vary depending on the underlying cause and the severity of the condition. Common symptoms may include:
Discoloration of the skin: The affected area may appear brown, reddish-brown, or bronze in color, resembling a stain on the skin. This discoloration is caused by the deposition of hemosiderin in the tissues after red blood cells are removed.
Swelling and Edema: In cases of venous insufficiency (poor lower leg blood flow), swelling and edema may occur in the affected limb due to fluid retention caused by impaired circulation.
Itching and Discomfort: Some individuals may experience itching or discomfort in the affected area, especially if the hemosiderin staining is associated with a skin condition such as eczema.
Ulceration: In severe cases of venous insufficiency, chronic skin changes may lead to the development of ulcers, particularly around the ankles.
Diagnosing hemosiderin staining typically involves a physical examination and medical history review by a healthcare professional. In some cases, additional tests may be necessary to determine the underlying cause and extent of the condition. These may include:
Visual evaluation combined with medical history: If the medical history involves one of the previously mentioned causes and the area looks like cloudy brown discoloration, the issue may be identified as hemosiderin staining.
Doppler Ultrasound: This non-invasive imaging test uses sound waves to evaluate blood flow in the veins and identify any abnormalities or blockages that may be contributing to venous insufficiency.
Skin Biopsy: A small sample of skin tissue may be taken and examined under a microscope to confirm the presence of hemosiderin deposits and rule out other skin conditions.
Blood Tests: Blood tests may be conducted to assess iron levels and screen for underlying iron overload disorders such as hemochromatosis.
The treatment of hemosiderin staining in some cases aims to address the underlying cause and alleviate symptoms and in other cases treats the present condition only (usually cosmetic procedures). Depending on the severity and nature of the condition, treatment options may include:
Laser Treatment: In the case of hemosiderin staining due to sclerotherapy injections, eye and nose surgery as well as facial injection procedures, q-switched Nd: Yg lasers can be used to break up and remove the hemosiderin particles beneath the skin.
Compression Therapy: Compression stockings or bandages may be prescribed to improve venous circulation and reduce swelling in individuals with venous insufficiency.
Elevation: Elevating the affected limb above heart level can help reduce swelling and improve blood flow.
Topical Treatments: Emollients, moisturizers, or topical corticosteroids may be recommended to soothe itching and inflammation associated with hemosiderin staining.
Wound Care: For individuals with venous ulcers, proper wound care techniques such as cleaning, dressing changes, and topical medications may be necessary to promote healing and prevent infection.
Iron Chelation Therapy: In cases of iron overload disorders, medications known as iron chelators may be prescribed to help remove excess iron from the body and prevent further deposition of hemosiderin.
Surgical Interventions: In severe cases of venous insufficiency or chronic ulcers, surgical procedures such as vein ligation, sclerotherapy, or skin grafting may be considered to improve circulation and promote wound healing.
Hemosiderin staining is a common condition characterized by the accumulation of hemosiderin in tissues, often secondary to venous insufficiency, trauma, or chronic inflammation. While typically benign, hemosiderin staining can cause cosmetic concerns and discomfort in some individuals. Prompt diagnosis and appropriate management are essential to address underlying causes, alleviate symptoms, and prevent complications. Individuals experiencing symptoms of hemosiderin staining should seek medical evaluation for proper diagnosis and treatment guidance.
